
Due to the nature of the assumptions in the model for drawdown using the Theis equation, it is most commonly used for single well analysis. Assumptions underlying all of the derivations must be taken into consideration also. To ensure the performance and efficiency of the well and the protection of the aquifer being pumped from requires many tests and a careful study of all the factors invloved. The calculation of the cone of depression for different pumping rates for various periods of time is just one small part of a many faceted and detailed evaluation of a potential well site. High and low storativity both create a wide cone with the low storativity having a deeper v-shape.įigure 5: Effects of Storativity and Transmissivity on the Cone of Depression Low transmissivity produces a tight ``v'' shape, while high transmissivity pulls the cone out into a wider, more shallow shape. Drawdown at any point at a given time is directly proportional to the pumping rate and inversely proportional to aquifer transmissivity and aquifer storativity.'' Figure 5 illustrates these relationships between high and low transmissivity and storativity. ``For a given aquifer the cone of depression increases in depth and extent with increasing time. A plot of the cone of depression can be calculated using values of or the drawdown at various values of r for a given time t. If T, S, and the pumping rate Q are known for the aquifer, the drawdown can be easily calculated. Storativity is the addition or release of water to the storage space due to the increase or decrease of hydraulic head, while transmissivity is a function of the hydraulic conductivity and the thickness of the aquifer and descibes how easily the aquifer moves groundwater through its pore spaces. The exponential integral is easily calculated with u defined as above and is known as the Well Function, W(u).
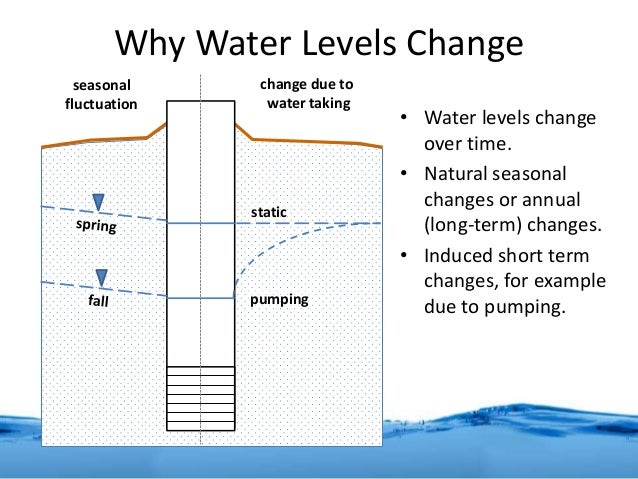
This drawdown generates a cone- or funnel-shaped depression called a cone of. In doing so, pumping causes a reduction in hydraulic head, known as drawdown. = drawdown at distance( r) at time ( t) after the start of pumping Įuler`s constant =. Cones of Depression: Pumping at a well, or at a wellfield, pulls water toward the well from all directions in other words, it induces radial flow (around the radius of the well). Drawdown at any point at a given time is directly proportional to the pumping rate and inversely proportional to aquifer transmissivity and aquifer storativity. The Theis equation has become the most widely used equation in transient groundwater hydraulics and the solution in terms of drawdown is Theis found the non-steady flow of groundwater to be analagous to the unsteady flow of heat in a homogeneous solid. He developed an analytic solution for the drawdown for a non-steady flow in a confined aquifer. Theis first published in 1935 ``The Relation Between the Lowering of the Piezometric surface and the Rate and Duration of Discharge of a Well Using Groundwater Storage''. What is the drawdown?Ī well has a calculated specific capacity of 30 gpm per foot and operates at a flow rate of 1.08 MGD.Next: Hydraulic Conductivity Up: Radial Flow to Previous: Radial Flow toĬ.V. The well operates at a constant 1,500 gpm. What was the average specific capacity for the year?Ī well has a specific capacity of 42 gpm per foot. The pumping level averaged 55 ft bgs for half the year and 68 ft bgs the other half. For half the year the static water level was 25 ft bgs and half the year 42 ft bgs. If the original drawdown was 42 ft what is the current specific capacity?Ī well pumped 538 AF over a one year period averaging 10 hours of operation per day. In addition, the drawdown has decreased by 15%. A straight line initially is regressed to drawdown and recovery data with the GROSS FIT button.


Analyzable drawdown and residual drawdowns are plotted on a semi-log plot.
#Drawdown definition hydrogeology series#
The efficiency of the well has dropped 35%. A continuous series of antecedent, pumping, and recovery water levels in the pumped well are specified as depth to water or water level above the transducer. When a well was first constructed it was pumping 1,750 gpm. After 3 hours of operation, the well produced 279,000 gallons. What is the pumping level of the well?Ī well has an hour meter attached to a water meter totalizer. A drawdown has been calculated out to be 65 ft.
If the drawdown on this well is 44 ft and the pumping level is 80 ft bgs, what is the static water elevation above sea level?Ī deep well has a static water level of 122 ft bgs. What is the drawdown?Ī groundwater well has a base elevation of 1,125 ft above sea level. \)Ī well has a static water level of 23 ft bgs and a pumping level of 58 ft bgs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
